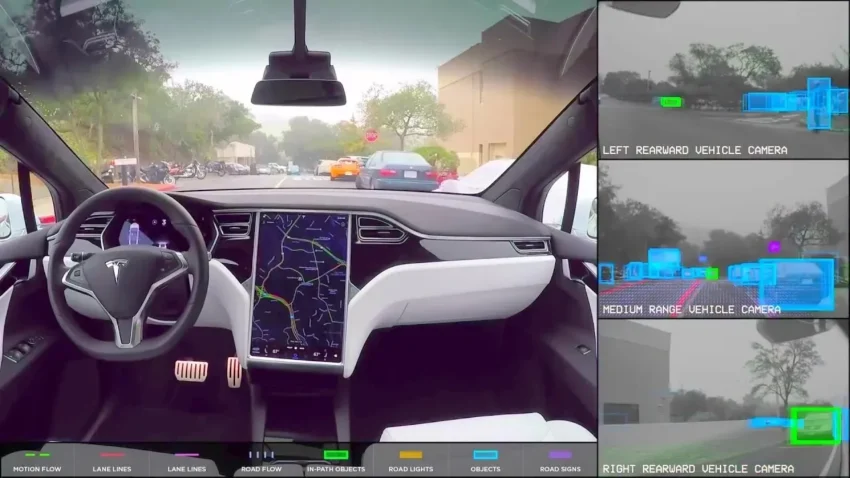
Self-driving vehicle testing has become a focal point of discussion as tech companies navigate the complexities of autonomous technology on public roads. Recent data from California’s Department of Motor Vehicles reveals that autonomous vehicle miles logged in 2024 dropped significantly, decreasing by 50% compared to the previous year. This decline is particularly evident in the realm of driverless vehicle permits, where testing miles plummeted by 83%. The DMV’s annual self-driving report highlights these trends, showcasing the challenges faced by key players like Waymo and the suspension of Cruise’s operations. As the landscape shifts, the future of autonomous vehicle testing remains uncertain, raising questions about safety, technology reliability, and market viability in an increasingly competitive environment.
The evaluation of autonomous driving technology is essential as the industry shifts towards a new paradigm. Known by various terms such as driverless vehicles and automated transport solutions, these innovations promise to revolutionize how we navigate our roads. However, with significant declines in testing activity and the tightening of regulations, the landscape for autonomous vehicle trials is changing rapidly. Companies are now facing scrutiny over their testing practices and safety standards, particularly highlighted in the DMV’s self-driving reports. As we explore the realm of driverless technology, understanding the implications of these trends is crucial for stakeholders and consumers alike.
Decline in Self-Driving Vehicle Testing
Recent data from California’s Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) reveals a significant decrease in self-driving vehicle testing on public roads, with a reported 4.5 million autonomous vehicle miles logged in 2024. This figure represents a staggering 50% decline from the previous year, highlighting a growing trend among tech companies to slow down their testing efforts. The DMV’s report categorizes these test miles into two distinct groups: those involving human safety drivers and those permitting driverless operations. Notably, the most drastic decrease occurred in driverless testing, which plummeted 83% from 3.26 million miles in 2023 to just 552,895 miles in the last year. This decline raises important questions about the future of autonomous vehicle technology and its readiness for public deployment.
The drop in testing miles reflects broader industry challenges, including regulatory scrutiny and safety concerns. As companies navigate the complexities of developing reliable autonomous systems, they face increasing pressure from both the DMV and the public to ensure the safety of these vehicles. The ongoing disengagement reports published by the DMV also contribute to the apprehension surrounding driverless vehicles, as they detail instances where human intervention was necessary due to technology failures. These reports, however, are often criticized for their inconsistency, making it difficult to gauge the actual proficiency of the technology across different companies.
The decline in self-driving vehicle testing is further exacerbated by the changing landscape of the industry. Major players like Cruise and Waymo have shifted their focus toward commercial endeavors, with Waymo transitioning into a robotaxi operator model. This shift in strategy indicates a pivot away from extensive testing in favor of refining their commercial operations. The DMV’s statistics reveal that only a handful of companies remain active in public road testing, with many having discontinued their testing programs altogether. As the market consolidates, the number of permits issued for testing vehicles with a human driver has dwindled significantly, reflecting an industry that is becoming increasingly cautious about its future prospects.
Impact of Cruise Suspension on Testing
The suspension of Cruise’s testing permits by the DMV has sent ripples through the autonomous vehicle industry, highlighting the precarious nature of self-driving vehicle development. After accumulating 2.6 million test miles in 2023, Cruise’s abrupt halt in testing following the permit suspension in October has left a notable void in the market. This situation exemplifies the challenges autonomous vehicle companies face in maintaining operational momentum in the face of regulatory hurdles and safety concerns. The incident serves as a stark reminder of the fragile balance between innovation and regulation in the development of autonomous driving technology.
With Cruise’s exit from California’s public road testing landscape, Waymo has emerged as one of the few remaining players actively logging significant autonomous vehicle miles. As the industry consolidates, the focus has shifted to companies that can navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance while also pushing forward with technological advancements. The impact of Cruise’s suspension underscores the importance of maintaining rigorous safety standards and the need for companies to adapt quickly to changing regulatory environments.
Moreover, the Cruise suspension reflects a broader trend in the autonomous vehicle sector, where regulatory scrutiny is becoming increasingly stringent. As companies grapple with the implications of safety reports and public perception, the path to successful deployment of driverless vehicles appears more complex than ever. The DMV’s stringent oversight and the public’s cautious stance toward self-driving technology necessitate that companies not only innovate but also demonstrate their commitment to safety and reliability. This scenario may lead to a more cautious approach in testing, as companies look to rebuild trust with regulators and consumers alike.
The Role of Waymo in the Autonomous Vehicle Landscape
Waymo has firmly established itself as a leader in the autonomous vehicle industry, particularly following its transition to a commercial robotaxi operator. As the company shifts its focus away from traditional testing to intensifying its commercial operations in cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles, it has set a precedent for what the future of autonomous driving may look like. With a significant investment of $5.6 billion raised in late 2023, Waymo is positioning itself to dominate the market, particularly in areas where consumer demand for driverless services is growing. This strategic pivot underscores the necessity for companies in the autonomous vehicle industry to adapt their business models in response to evolving market conditions and regulatory landscapes.
Despite the challenges faced by other companies in the autonomous vehicle sector, Waymo’s robust performance and commitment to safety have allowed it to maintain a competitive edge. The company has been able to log substantial autonomous vehicle miles, providing valuable data to refine its technology. As Waymo continues to expand its commercial operations, it also faces the responsibility of setting industry standards for safety and performance, potentially influencing regulatory frameworks that govern the entire sector.
However, Waymo’s dominance also raises questions about competition within the autonomous vehicle industry. With fewer companies actively testing and a notable reduction in the number of permits issued by the DMV, the landscape is becoming increasingly consolidated. This lack of competition could stifle innovation and slow advancements in the technology, as new entrants may find it challenging to secure the necessary permits and funding to compete effectively. As Waymo leads the way in both testing and commercial miles, the industry must remain vigilant to ensure that a balance is maintained—encouraging innovation while adhering to safety standards that protect the public.
Safety Concerns in Autonomous Vehicle Testing
Safety remains a pressing concern in the field of autonomous vehicle testing, particularly as companies navigate the complexities of developing reliable self-driving technology. The DMV’s annual disengagement reports highlight the number of instances where human drivers had to intervene, raising alarm about the readiness of these vehicles for public roads. The discrepancies in how different companies report disengagements further complicate the assessment of safety across the industry. Without standardized metrics, comparing the safety performance of various autonomous vehicle technologies becomes nearly impossible, leading to skepticism among regulators and the public alike.
In light of these concerns, companies must prioritize transparency and accountability in their testing processes. Demonstrating a commitment to safety through rigorous testing protocols and clear reporting practices will be essential for gaining public trust and regulatory approval. As the industry evolves, establishing uniform standards for safety reporting and operational performance will be crucial. This could pave the way for broader acceptance of autonomous vehicles, provided that companies can prove their technologies are safe and reliable.
Moreover, the path to achieving widespread public acceptance of autonomous vehicles is fraught with challenges. Public perception often hinges on high-profile incidents or failures associated with self-driving cars, leading to an uphill battle for companies striving to demonstrate the efficacy of their technologies. Continuous engagement with the public and transparent communication about safety measures and technological advancements can help mitigate these concerns. As companies work diligently to improve their autonomous systems, fostering a culture of safety and accountability will be paramount in overcoming the hurdles to widespread adoption.
Future of Driverless Vehicle Permits
The future of driverless vehicle permits in California appears uncertain, as recent data indicates a sharp decline in new permits issued by the DMV. From four permits in 2022 to just one in 2024, the trend reflects a cautious approach by regulators in response to safety concerns and the mixed results of autonomous vehicle testing. Currently, only six companies are authorized for driverless testing, and only a select few have been granted permits for commercial operations. This scarcity of permits raises significant concerns about the pace of innovation and development within the autonomous vehicle industry, as fewer companies are able to actively contribute to the advancement of driverless technologies.
As the industry grapples with regulatory constraints, emerging companies may find it increasingly challenging to enter the market. This could lead to a stagnant environment where only a handful of established players, like Waymo and Nuro, dominate the space. The limited availability of permits may discourage new investments and hinder the overall growth of autonomous vehicle technology, casting a shadow on the future of driverless vehicles in California and beyond.
However, this situation also presents an opportunity for established companies to refine their technologies and demonstrate their readiness for commercial deployment. By focusing on safety and performance, these companies can make a compelling case for the expansion of driverless vehicle permits in the future. As the regulatory landscape evolves, there may be room for new entrants who can meet stringent safety standards while also contributing to the innovation ecosystem. Ultimately, the future of driverless vehicle permits will depend on the industry’s ability to balance safety with the need for technological advancement.
The Consolidation of the Autonomous Vehicle Industry
The autonomous vehicle industry has experienced a significant consolidation over recent years, with many companies exiting the market or refocusing their efforts. The DMV’s report indicates a dramatic decline in the number of companies actively testing autonomous vehicles, dropping from around 60 to just 31 holding permits for testing with a human driver. This trend reflects broader market challenges, including the high costs associated with developing self-driving technology and the growing regulatory scrutiny that companies face. As a result, only a few players like Waymo and Cruise remain at the forefront of autonomous vehicle testing and development, emphasizing the need for companies to adapt swiftly to survive in this evolving landscape.
The consolidation has also led to an environment where competition is limited, potentially hindering innovation. With fewer companies vying for market share, the impetus to develop cutting-edge technologies may diminish. However, for the remaining players, this shift presents an opportunity to capitalize on their established positions and refine their technologies without the pressure of a crowded market. As the industry continues to evolve, it will be crucial for these companies to push the boundaries of autonomous vehicle technology while addressing safety and regulatory challenges.
Looking ahead, the consolidation of the autonomous vehicle industry may pave the way for strategic partnerships and collaborations among the remaining players. As companies seek to combine their strengths and resources, there may arise a new wave of innovation fueled by shared expertise and technology. This collaborative approach could lead to breakthroughs in safety and efficiency, ultimately benefiting the industry as a whole. The evolution of the autonomous vehicle sector will depend on the ability of these companies to navigate the complexities of the market while fostering a spirit of cooperation that drives progress in self-driving technology.
Investment Trends in Autonomous Vehicle Technology
Investment trends in the autonomous vehicle sector have shifted dramatically, with venture capital funding becoming increasingly selective. The exuberance of the past, which saw numerous startups entering the market, has given way to a more cautious approach as investors reassess the viability of self-driving technology. Notably, Wayve’s recent $1 billion funding round and Waymo’s $5.6 billion raise signal that while the industry may be consolidating, there is still significant interest in companies that demonstrate potential for growth and innovation. This trend highlights the importance of strategic investment as companies aim to navigate a challenging landscape while pushing the boundaries of autonomous vehicle development.
As funding becomes scarcer, companies must focus on demonstrating tangible results to attract investment. Investors are increasingly looking for evidence of successful technology deployment and a clear path to profitability. This shift in focus may lead to a greater emphasis on safety and performance metrics, as companies strive to showcase their capabilities in a competitive market. As the investment landscape evolves, the ability of companies to secure funding will hinge on their ability to deliver reliable and innovative solutions in the realm of autonomous vehicles.
Moreover, the changing investment climate may encourage established companies to pursue strategic collaborations and joint ventures to pool resources and expertise. By coming together, companies can share the financial burden associated with research and development while also enhancing their technological capabilities. This collaborative spirit may lead to accelerated advancements in autonomous vehicle technology, as companies leverage each other’s strengths to overcome shared challenges. As the industry adapts to the complexities of the market, the focus on strategic partnerships will be essential for driving future innovation and ensuring the continued growth of the autonomous vehicle sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the latest DMV self-driving report indicate about autonomous vehicle miles in California?
The latest DMV self-driving report highlights a significant decline in autonomous vehicle miles, with a total of 4.5 million miles logged in 2024, marking a 50% decrease from the previous year. This decrease is primarily driven by an 83% drop in driverless testing miles, which fell from 3.26 million to just 552,895 miles.
How has the Cruise suspension affected self-driving vehicle testing in California?
The Cruise suspension has notably impacted self-driving vehicle testing in California, particularly as Cruise had previously logged 2.6 million test miles in 2023. After the suspension of its permits in October 2023, Cruise has not resumed testing, contributing to the overall decline in testing activities.
What are the current trends in driverless vehicle permits issued by the DMV?
Current trends show a drastic reduction in driverless vehicle permits issued by the DMV. In 2024, only one new permit was issued for testing with a safety driver, compared to four permits in 2022 and two in 2023. This reflects a tightening of regulations and fewer companies actively testing on public roads.
How do Waymo’s operations differ from traditional self-driving vehicle testing?
Waymo has transitioned from traditional self-driving vehicle testing to focusing on commercial operations, particularly in San Francisco and Los Angeles. This shift means that while Waymo has logged significant testing miles, it is now prioritizing its role as a commercial robotaxi operator over extensive testing.
What role do disengagement reports play in self-driving vehicle testing?
Disengagement reports are crucial for self-driving vehicle testing as they document instances where human drivers must take over due to technology failures or safety issues. However, these reports have been controversial because different companies use varying standards, making it difficult to compare the performance of their autonomous technologies.
Why has there been a consolidation in the self-driving vehicle industry?
The consolidation in the self-driving vehicle industry, which began around 2019, can be attributed to decreased venture capital availability and heightened scrutiny of safety and efficacy. As a result, fewer companies are willing to invest heavily in autonomous vehicle technology, leading to a significant reduction in active participants.
What are the implications of Tesla not logging any autonomous miles in the recent DMV report?
Tesla not logging any autonomous miles in the recent DMV report raises questions about its current self-driving vehicle testing strategy and capabilities. This absence signals a potential shift in focus or challenges faced by Tesla in the competitive landscape of autonomous vehicle technology.
Which companies currently hold permits for driverless vehicle testing?
As of now, six companies including AutoX, Nuro, WeRide, Waymo, and Zoox hold permits for driverless vehicle testing. Notably, only Mercedes-Benz, Nuro, and Waymo have permits that allow for commercial operations, highlighting the stringent regulatory environment in the autonomous vehicle sector.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Tech companies have reduced self-driving vehicle testing on California roads by 50% in 2024 compared to 2023. |
| A total of 4.5 million autonomous vehicle test miles were logged in 2024, with a significant decrease in driverless testing (83%). |
| The DMV reported that only 31 companies currently hold permits for testing, with only 11 conducting public road tests in 2024. |
| Waymo and Cruise are the major players, with Waymo focusing on commercial operations and Cruise ceasing testing due to permit suspension. |
| The issuance of new permits has drastically decreased, with only one new permit issued in 2024. |
| The industry has experienced consolidation, with fewer companies willing to invest heavily in autonomous vehicle technology. |
Summary
Self-driving vehicle testing has seen a significant downturn, with a 50% reduction in test miles logged in California in 2024 compared to the previous year. This decline reflects broader trends in the industry, including a decrease in the issuance of new testing permits and a consolidation of major players focusing on commercial operations. As the market evolves, fewer companies are actively engaged in testing, highlighting a shift in the landscape of self-driving vehicle technology.