Telecom competition has reached a pivotal moment as emerging technologies and consumer preferences disrupt the traditional landscape dominated by cable monopolies. Companies like Comcast and Charter, once the unchallenged giants of broadband access, are now grappling with the rise of 5G wireless services and community broadband initiatives that offer consumers viable alternatives. As more users shift away from overpriced cable packages, these telecommunications behemoths face significant subscriber losses, prompting discussions around potential mergers like the rumored Charter Comcast merger. The competitive environment is further intensified by the rapid adoption of home 5G services, which are proving to be a formidable challenge to conventional cable offerings. With the stakes higher than ever, the future of telecom competition is poised for transformation, benefiting consumers who seek affordable and high-quality connectivity options.
The landscape of telecommunications is undergoing a dramatic shift as new players enter the fray, challenging the long-standing dominance of traditional cable providers. With the advent of advanced wireless technologies and community-driven broadband solutions, the era of cable monopolies is increasingly being questioned. As consumers embrace alternatives such as 5G networks, the competitive dynamics are shifting, forcing established companies to rethink their strategies in order to retain market share. The potential for significant mergers, like that between Charter and Comcast, highlights the urgency felt by these corporations in the face of dwindling subscriptions and rising competition. Ultimately, this transformation in the telecom sector not only reshapes the market but also empowers consumers with greater choice and better pricing.
The Rise of 5G Wireless Services: A Game Changer for Broadband Access
5G wireless services are rapidly transforming the telecommunications landscape, offering consumers a viable alternative to traditional cable broadband. With speeds that can rival or exceed those of cable, 5G technology is empowering users to make informed choices about their internet service providers. This shift is particularly significant as more customers are seeking options that provide not only better pricing but also enhanced service quality. As cable monopolies like Comcast and Charter lose ground, the appeal of home 5G solutions becomes increasingly apparent, especially in areas where cable access remains limited.
Moreover, the competitive pressure from 5G wireless service providers is prompting traditional cable companies to rethink their strategies. The surge in demand for wireless alternatives is forcing companies to enhance their offerings, potentially leading to better pricing and customer service for consumers. As this technology continues to advance and become more widely available, it may disrupt the long-standing dominance of cable providers and encourage a more competitive and consumer-friendly market.
Telecom Competition: Challenging the Cable Monopolies
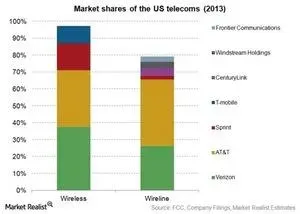
The competitive landscape of the telecom industry is evolving as new players enter the market, challenging the established cable monopolies. With companies like AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile actively expanding their 5G offerings, the once-uncontested reign of cable giants like Comcast and Charter is coming to an end. The recent loss of millions of broadband and TV customers by these companies signals a fundamental shift in consumer preferences. As people increasingly choose more affordable wireless solutions, the pressure mounts on cable providers to innovate or risk obsolescence.
This increasing telecom competition is not merely beneficial for consumers; it also fosters a healthier market environment overall. With more options available, consumers can demand better service and pricing, which ultimately leads to improved quality across the board. However, the challenge remains for new entrants to maintain competitive pricing without compromising service quality, as established giants often have the advantage of economies of scale. The ongoing evolution of telecom competition will be crucial in reshaping the future of broadband access, pushing cable companies to reassess their business models.
Community Broadband: A Growing Alternative
Community broadband initiatives are gaining traction as a formidable alternative to traditional cable services. These locally-owned networks often provide faster and more reliable internet access at lower prices than their corporate counterparts. As municipalities invest in community broadband, they address the shortcomings of cable monopolies, particularly in underserved areas where access to quality internet is limited. This movement not only enhances connectivity but also empowers local governments to take control of their internet infrastructure.
Furthermore, community broadband projects have the potential to stimulate local economies by providing residents and businesses with the reliable internet access they need to thrive in a digital age. As more cities and towns recognize the benefits of these networks, the influence of large cable companies may wane, giving way to a more distributed and equitable approach to broadband access. The rise of community broadband signifies a shift toward prioritizing the needs of consumers over corporate profits, creating a more sustainable and inclusive internet landscape.
The Impact of the Charter-Comcast Merger Speculation
The speculation surrounding a potential merger between Charter and Comcast has sparked conversations about the future of telecommunications in the United States. While executives may see this as a way to stabilize their companies amid declining customer bases, such consolidation typically leads to adverse effects for consumers. Mergers often result in higher prices, diminished service quality, and reduced competition, which contradicts the very principles that should govern a healthy telecom market.
Moreover, the fear is that a Charter-Comcast merger could further entrench existing monopolies, leaving consumers with fewer choices and even less leverage in negotiations for better pricing and service. As history has shown, the consolidation of power in the telecom sector tends to stifle innovation and hinder the emergence of new competitors. Therefore, while the prospect of a merger may seem appealing to shareholders in the short term, it poses significant long-term risks to the competitive landscape and consumer welfare.
The Role of Federal Oversight in Telecommunications
Federal oversight plays a crucial role in ensuring a fair and competitive telecommunications market. The erosion of consumer protections under the current administration has raised concerns about the future of broadband access in the U.S. As regulations like net neutrality are dismantled, telecom companies are given the freedom to prioritize profits over consumer needs, leading to potential abuses in pricing and service quality. A lack of oversight can significantly hinder competition, allowing monopolies to thrive unchallenged.
Without robust federal regulations, consumers may find themselves at the mercy of telecom giants that have little incentive to compete on price or service quality. The absence of meaningful consumer protections can lead to a market where companies exploit their dominant positions, further entrenching inequities in broadband access. Restoring and enhancing federal oversight is essential for creating an environment where competition can flourish, ultimately benefiting consumers and promoting equitable access to essential communication services.
The Threat of Cable Monopolies and Their Future
The threat posed by cable monopolies like Comcast and Charter is increasingly challenged by new technologies and market dynamics. As consumers become disenchanted with traditional cable services, the rise of alternatives like 5G wireless and community broadband is reshaping the competitive landscape. However, these cable giants still retain significant market power, particularly in areas where they have established monopolies. Their ability to adapt and respond to this growing competition will determine their survival in the evolving telecom ecosystem.
Despite facing pressure from competitors, cable monopolies continue to leverage their existing infrastructure to maintain dominance. Their efforts to expand into mobile wireless services indicate a recognition of the shifting market landscape. Yet, as consumers increasingly prioritize value and quality, the sustainability of these monopolies is called into question. The future of cable companies hinges on their ability to innovate and provide services that align with consumer preferences, as the landscape continues to evolve.
Consumer Preferences: Shifting Away from Cable Providers
Consumer preferences are shifting dramatically as more people seek alternatives to traditional cable providers. The rise of streaming services and the increasing availability of affordable 5G wireless options are driving this transformation. Many customers are choosing to cut the cord, opting for internet services that offer greater flexibility and lower costs. This trend poses a significant challenge to cable companies, which must adapt to changing consumer demands or risk losing relevance in the market.
As users become more informed about their options, cable providers are forced to respond by enhancing their offerings and potentially lowering prices. The growing dissatisfaction with high cable bills and poor service quality is prompting consumers to explore more competitive alternatives. This shift not only benefits individual users but also contributes to a more dynamic and competitive telecommunications landscape, ultimately fostering an environment where consumer needs take precedence over corporate profits.
Infrastructure Investment: The Future of Broadband Access
Infrastructure investment is critical to expanding broadband access across the United States. The recent infusion of $42.5 billion in infrastructure funding presents an opportunity for states to bolster their internet infrastructure, particularly in underserved areas. However, there are concerns that much of this funding may be diverted toward established telecom giants instead of supporting community-based broadband initiatives. Ensuring that these funds are allocated effectively is essential for creating a more equitable internet landscape.
Investing in broadband infrastructure not only enhances connectivity but also stimulates economic growth by enabling businesses and individuals to thrive in a digital world. The focus should be on supporting innovative solutions like municipal broadband networks and community-owned initiatives that prioritize affordability and access for all. As infrastructure investments are made, the potential for significant improvements in broadband access and competition can reshape the future of telecommunications in the U.S.
The Future of Telecom: Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
The future of the telecom industry is poised for both opportunities and challenges as new technologies and consumer preferences reshape the landscape. The rise of 5G wireless services and community broadband initiatives presents a chance to enhance competition and provide consumers with more choices. However, the legacy of cable monopolies and the potential for further consolidation pose significant threats to the progress being made in expanding broadband access.
As the industry evolves, stakeholders must remain vigilant in advocating for policies that promote competition and protect consumer rights. This includes pushing for the restoration of federal oversight and ensuring that infrastructure investments benefit a broad range of communities. Navigating the complexities of the telecom landscape will require collaboration among consumers, local governments, and policymakers to create an environment that fosters innovation, equity, and access to essential communication services.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does telecom competition impact the pricing of 5G wireless services?
Telecom competition plays a crucial role in determining the pricing of 5G wireless services. As companies like Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile compete for market share, they often reduce prices to attract customers from traditional cable monopolies like Comcast and Charter. However, this price reduction may be temporary, as providers could raise prices once they have secured a significant customer base. Therefore, increased competition can initially lower costs for consumers but may lead to higher prices in the long run.
What role do cable monopolies play in the current telecom competition landscape?
Cable monopolies, particularly Comcast and Charter, have historically dominated broadband access, limiting competition in many areas. However, the rise of community broadband initiatives and 5G wireless services is challenging their monopoly. As consumers seek alternatives due to rising dissatisfaction with traditional cable services, these monopolies are losing customers, leading to a more competitive telecom landscape.
What is the impact of the Charter Comcast merger on telecom competition?
The potential Charter Comcast merger raises concerns about the impact on telecom competition. Mergers in the telecom sector often lead to reduced competition, resulting in higher prices, lower service quality, and fewer choices for consumers. If the merger goes through, it could further consolidate power among cable monopolies, diminishing the competitive threat posed by emerging technologies like community broadband and 5G wireless services.
How are community broadband initiatives changing the telecom competition dynamics?
Community broadband initiatives are significantly changing the telecom competition dynamics by providing local alternatives to traditional cable services. These initiatives often offer faster and more affordable internet options, challenging the dominance of cable monopolies. As more municipalities invest in their broadband access, consumers gain additional choices, which can drive down prices and improve service quality in the telecom market.
What are the long-term effects of telecom competition on broadband access?
Long-term effects of telecom competition on broadband access can lead to improved service quality, lower prices, and increased innovation. As companies compete, they are incentivized to enhance their offerings and expand their networks. However, if monopolies or oligopolies dominate the market, consumers may face higher costs and fewer options, which emphasizes the importance of maintaining robust competition in the telecom sector.
How does the shift towards 5G wireless services affect broadband access competition?
The shift towards 5G wireless services is enhancing competition in broadband access by providing consumers with faster and more affordable options compared to traditional cable services. As major telecom providers expand their 5G offerings, they are attracting customers who previously relied on cable monopolies. This transition can lead to a more competitive environment, pushing cable companies to innovate and potentially lower prices to retain their customer base.
What challenges do cable monopolies face in the current telecom competition environment?
Cable monopolies like Comcast and Charter face several challenges in the current telecom competition environment, including the rise of 5G wireless services, community broadband alternatives, and shifting consumer preferences. As more users opt for alternative internet sources, these companies risk losing significant market share, prompting them to adapt their business strategies to maintain profitability and customer loyalty.
How does federal oversight affect telecom competition in the U.S.?
Federal oversight plays a crucial role in shaping telecom competition in the U.S. Regulations enforced by the FCC and other agencies can promote fair competition, prevent monopolistic practices, and protect consumer rights. However, as oversight diminishes, telecom companies may have less incentive to compete on price and service quality, which could lead to negative outcomes for consumers, such as higher costs and lower service standards.
What is the outlook for telecom competition with the rise of 5G and community broadband?
The outlook for telecom competition is generally positive with the rise of 5G and community broadband initiatives. These developments are fostering a more competitive environment, giving consumers more choices and potentially driving down prices. However, the actual impact will depend on how regulatory frameworks adapt and whether cable monopolies can respond effectively to these emerging challenges.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Telecom Competition Landscape | Historically dominated by cable monopolies like Comcast and Charter, which profited despite losing traditional TV customers. |
| Emergence of 5G | The introduction of 5G wireless technology is providing competitive alternatives to cable broadband. |
| Consumer Shift | Many consumers are switching to home 5G services, leading to significant losses for traditional cable companies. |
| Stock Market Impact | The losses in customers have resulted in declining stock prices for cable companies, prompting speculation about mergers. |
| Mergers and Consolidation | Consolidation often leads to negative outcomes like higher prices and lower customer service quality. |
| Government Regulation | Dismantling of federal regulations has reduced consumer protections, giving telecoms less incentive to compete on pricing. |
| Community Broadband | Municipal and community-owned broadband networks pose a growing threat to traditional telecom giants. |
Summary
Telecom competition is intensifying as traditional cable monopolies face challenges from emerging technologies and new alternatives. The rise of 5G services has led to a significant shift in consumer preferences, with many users opting for more affordable wireless options over traditional broadband. As cable companies like Comcast and Charter struggle with declining customer bases and stock prices, the landscape is ripe for further consolidation—often at the expense of service quality and competitive pricing. Additionally, the erosion of federal oversight has left consumers vulnerable to exploitative practices. As municipalities expand their fiber networks, the potential for real competition increases, highlighting the need for stronger consumer protection measures in the telecom sector.